The Google knowledge graph is turning 10 in 2022!
This feature created quite the upstart when Google introduced it in May 2012. Since its addition, this little knowledge box that appears on the right (on top for mobile) of search results has gone through many changes.
The Google search knowledge graph is now on mobile. And according to Google, it has over 500 billion facts in its database.
Not sure what the Google knowledge graph is? If it all sounds confusing, we can assure you, its not something you need an IT professional to unravel.
We’ll go over a brief history of the popular tool, discuss how Google sources its knowledge base, and how you can try to use it for your SEO strategy.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
Table of Contents
What Is the Google Knowledge Graph?
Google introduced the Google knowledge graph in 2012 to quickly display facts and knowledge users search for. Technically, the graph is Google’s database with the information shown in knowledge panels.
The Basics
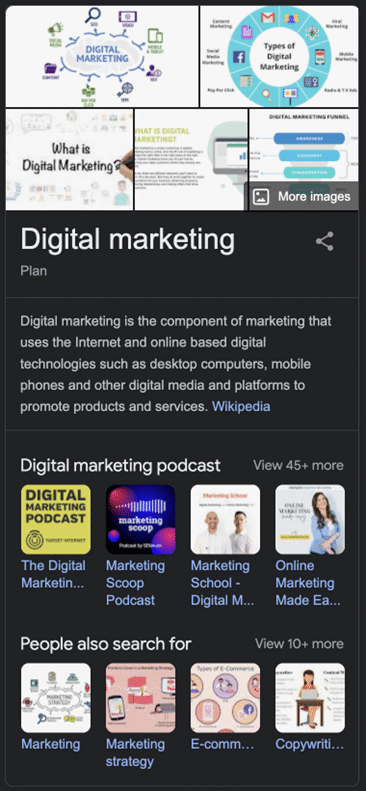
The Google search Knowledge Graph is a database designed to make it easier to find commonly searched information. It’s called a graph as it displays all the related information, not only the exact search terms entered.
The graph links related topics together. When you search for an author, say, William Shakespeare, you will also see information on some of his plays, popular movie adaptations, similar writers, and other people from his life.
All this information is displayed in the knowledge panels located at the top of the screen. Everything is displayed without needing to visit a third-party website, making the tool quick and convenient for fact-checking.
Behind the Scenes
The knowledge graph works by sourcing information from all over the internet, much of it from Wikipedia and Wikidata. Still, Google also claims to have its own index with hundreds of sources. It also uses Schema markups to better answer these questions and create the links between data.
Google displays these snippets at the top or right of the results page, depending on a user’s device. In smartphones, Google breaks up the knowledge panel into a few pieces, so Google search results aren’t shoved down too far.
The information displayed in the Google knowledge panel includes answers to common questions like “What day of the week was March 3rd, 2014?” or “Who was the first person on the moon?”
However, changes in the Google algorithm have led to an increase in the displayed information. Google now shows more related information than before. It has increased the links to related third-party pages, especially social media pages and shopping options.
The User Experience
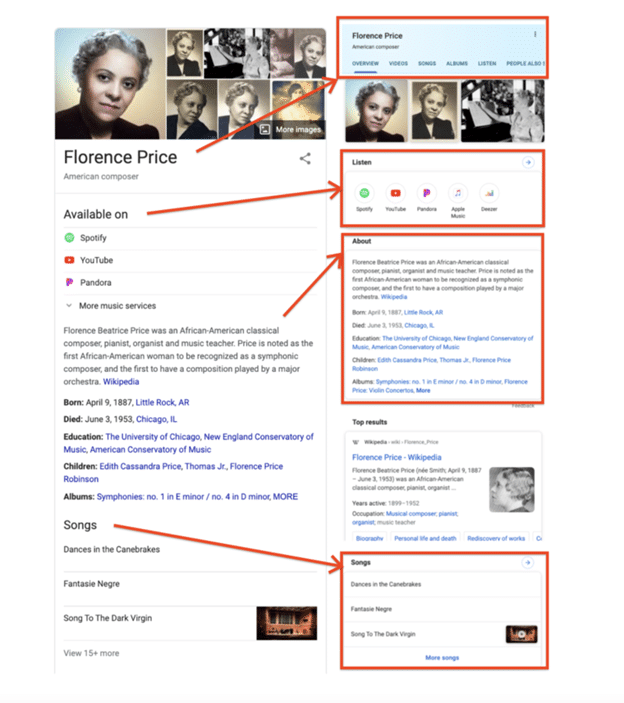
Googling the search term “How tall is the statue of liberty” will not only answer that question but also show you who built it, link to additional information, and display multiple photos of the statue, all from within the Google knowledge graph.
You can even get social profiles or direct links to Wikipedia pages, depending on your search query. Searching for locations will usually display a Google Maps snippet. But all this depends on the information Google has on a given query.
Google’s 2021 changes included changing the Google My Business tool to Google Business Profiles. Users can now verify information about their business that shows up in the Google knowledge graph — just make sure you have a verified Google profile.
Limitations of the Google Search Knowledge Graph
Now that we’ve gone over what the Google knowledge graph is, let’s look into some of its limitations. Google has addressed many of the early issues, and it continues to improve the knowledge graph, but no tool is perfect.
Main Issues With Google Knowledge Graph
- Small space to convey information — The space of one or two paragraphs doesn’t do justice to many complicated topics. This problem of limited space is even more evident on mobile devices than on desktops.
- Early criticism included lack of sources — When Google introduced the knowledge graph, it didn’t display the information sources. This stopped users from verifying the information. Google now displays the source links.
- Controversial “facts” — The Washington Post pointed out that Google’s sources can be inaccurate. Simple facts, like the height of Hilary Clinton, had multiple answers, ranging from 5 feet to 5 feet 6 inches, depending on the source.
- Reduced traffic concerns — Some critics raised concerns that the knowledge graph would reduce traffic to webpages Wikipedia, in particular, suffered a substantial traffic drop.
The Google search knowledge graph and the panels it displays are compiled largely by an algorithm. Without human checks, changes to the information can be slow and don’t always address issues raised.
These algorithms also control how the knowledge graph makes new connections. Because of this, connections can seem a bit strange or limited at times.
For example, searching for pyramids will display the great pyramids of Egypt, but related topics are not other pyramids but other famous landmarks. Without enough data linking the two topics, Google can’t make the connection in the knowledge graph.
It’s also worth adding that “zero-click” searches are rising. This search practice where users don’t click on any results is a big problem for SERPs. Zero-click Google searches rose to 65% of all searches in 2020, but it’s unclear which factors drive this trend.
Working With the Google Knowledge Graph
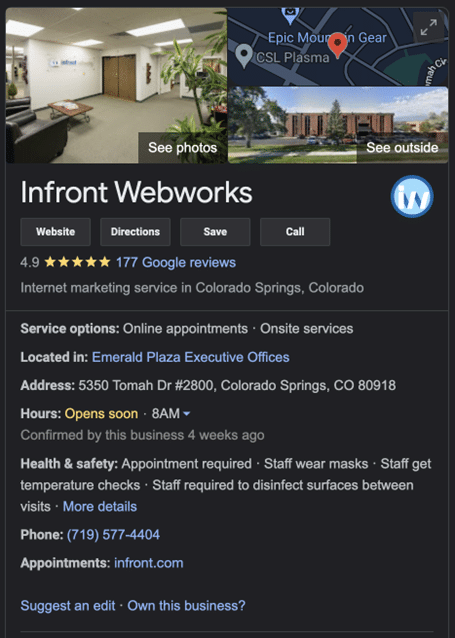
Despite its limitations, the Google knowledge graph is doing well. It’s expanding its focus and now displays even more information, including business-related data that business owners should benefit from.
While Google states that it maintains Google search knowledge graphs via “automatic systems,” it does allow individuals to submit updates.
To do so, you need to be verified with Google, usually through your organization. Then you can suggest edits to the information, photos, and links included in the knowledge graph on the company in question. This is especially useful for updating business hours and displaying changes in services.
If you want to improve the information on your company, Google recommends using the Google My Business tool. Google will source information about your business from GMB to add to your Google knowledge graph.
It’s important to note you cannot suggest new information for Google to use. Google also removes anything that qualifies as advertising, so stick to the facts. Consider adding your social media profiles (including your Linkedin) and update photos to include real-world views.
What Your Business Can Do With the Knowledge Graph
Add as much information as you can to your Google Business Profile to improve your standing on local searches and leave a good impression.
HubSpot found that 72% of consumers who performed a local search then visited a business within five miles of their location. These profiles have replaced the yellow pages, and searchers use them in much the same way.
As a business owner, you have a lot more information than just a telephone number you can add. Don’t forget to check your Business Profile insights. Google will show you how your business is performing in Google searches and how customers interact with your profile.
Think of the Google knowledge graph as an addition to your content marketing strategy, not something you do instead. It will help with your metrics, especially with local users, but it won’t get you the same traffic that an SEO strategy can provide.
Final Thoughts: What Is the Google Knowledge Graph and How Can It Help You?
The Google knowledge graph is a great way to quickly find the information you want from search engine results. While this feature started as a source for fact-checking, it has evolved into the go-to place to find out more about a topic, with an ever-expanding database of information available.
When incorporating the Google search knowledge graph into your SEO strategy, ensure your Google Business Profile has all the information a visitor might want to know. Try to update your profile every few months, even if it’s just to add some new pictures.
While a Google knowledge graph can help you stand out in results, it’s not a substitute for high-quality content. Google itself reminds users they can request a takedown if the information is inaccurate, but what information takes its place is entirely up to Google.
Don’t obsess over a mostly automated system when you have greater control over your website. You’ll find better ROI from a strategy aimed at a comprehensive SEO plan.

Matthew is the President of Infront Webworks and is a New England native now calling Colorado Springs home. Matt attended The University of NH where he pursued a BS in Natural Resource Economics & Business Administration. Aside from Infront; Matthew has owned and managed two other online agencies based on the seacoast of New Hampshire and been a key player in multiple technology mergers & acquisitions. When he’s not bathing in technology, online marketing & business; he’s probably spending time with his wife and daughter, boating, skiing the trees, hiking or cooking..he is a foodie for sure!